Did you know that scientists can now map our entire genes? That is, they can find out which gene is where and which disease or physical characteristic it is linked to. Earlier this process was very expensive and time consuming, but today technology has made it much faster and cheaper. Human genes mapping not only facilitates the diagnosis of diseases but also recommends the best medicine, which is suitable only for you. All of this is now possible because in July 2025, a new “best-ever” genome map was announced, that offers an incredible look at the complexities of human DNA.
This article will make the entire process of human genes mapping completely easy for you. We’ll cover what it is, how it works, what it costs, and how it’s shaping the future of medicine. Whether you’re a curious student, a science enthusiast, or just want to understand your genetic health, this guide will make a complex topic simple and valuable. So let’s get started.
The Basics of Human Genes Mapping
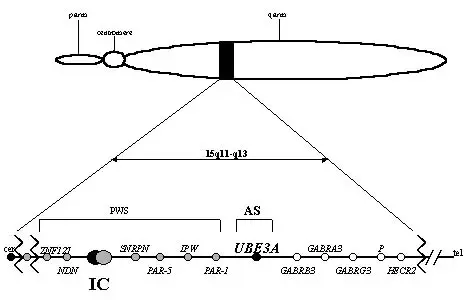
Genes mapping is the process of finding genes and key spots on a chromosome. Think of your genome as a giant instruction book for your body, made up of 23 parts (chromosomes). Gene mapping is like making a list that shows where each instruction (gene) is located. It is not like gene sequencing, which means writing out each word in the instruction book letter by letter.
There are two main types of gene mapping:
- Genetic Mapping: This method looks at how many times two genetic markers, which are sequences of a particular DNA sequence, have passed together. If they are close together on a chromosome, they are more likely to be inherited together. This helps scientists create a genetic map that shows how far apart genes are, for example, like markers used to map a highway.
- Physical Mapping: This technique helps measure the actual distance between genes in the base pairs of DNA. It is more accurate and was the main focus of the Human Genome Project. I can give you an example of this like using a GPS to find the exact address of a street.
To understand this difference between these two types is very important because it tells how scientists are working on the latest projects and which technology is widely used.
How Genes Mapping Works?
Here, the question that will arise in anyone’s mind is how the mapping is done. It is a technical process that has been divided into easy steps so that this mapping technique can be easily understood. Modern workflows, especially in 2025, rely on advanced technology and powerful computing.
Step 1: The Sample Collection
To start this process, a sample is first collected, for which a saliva or cheek swab is taken from us. As you know, our cells are the exact copies of the DNA of our entire body. All cells are the same, that is why scientists only need a small sample for testing. It can be illustrated as if there is a library of trillions of similar books from which one book is picked.
Step 2: DNA Extraction and Preparation
In this process, DNA is carefully separated from cells in a laboratory. For this process, experts use a powerful machine called a DNA sequencer. For large-scale projects, this involves whole-genome sequencing, which reads the entire DNA sequence from start to finish. Modern technologies, such as long-read sequencing, are making this process faster and more accurate than ever before.
Step 3: The Sequencing Marathon
This is where the magic really happens. High-tech machines read our genetic code one letter at a time. Imagine a high-speed reader going through billions of pages, noting every A, T, G, and C (the four letters of the genetic code). Today’s machines can read the entire human genome in about a day, while it took years during the first Human Genome Project.
Step 4: Computational Analysis
Raw genetic data seems meaningless – billions of characters with no obvious meaning. Powerful computers compare your sequence to the genome, identifying genes and mapping their locations. It’s like a super-smart librarian who can instantly sort through millions of books and tell you what’s in each one.
Step 5: Creating Your Personal Map
The final step involves turning the data into insights. Scientists create visual maps that show where your genes are located and how they differ from the average human genome. These maps highlight important variations that can affect your health, ancestry, and other traits.
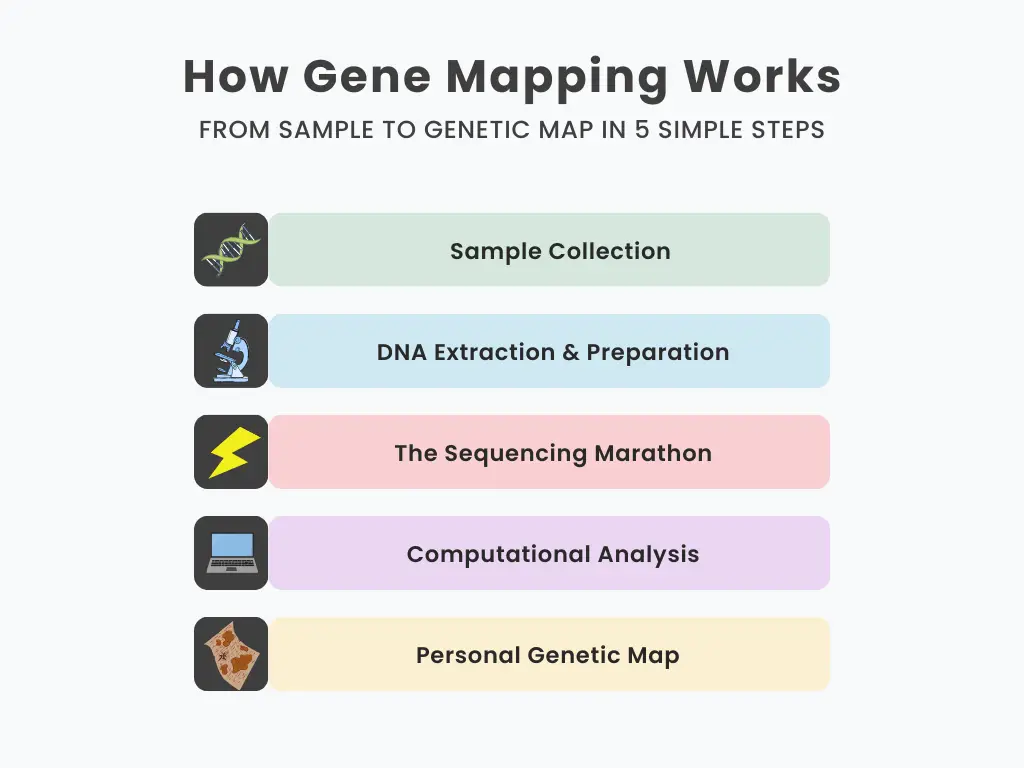
A process takes about two to four weeks to complete. It depends on the depth of the requested analysis, how deep the testing should be, and what you need to find out. In this sense, a process takes time. Although, it usually takes two to four weeks.
The Cost of Mapping Human Genes
Just as the advancements in mapping technology have been the same, the price has also come down. Now even ordinary people can get their genes mapped. Some time ago, the first gene mapping that was done cost up to $3 billions for one person, but now the prices for gene mapping have come down so much that anyone can get it done.
Consumer-Level Mapping
Basic genetic testing kits like 23andMe or AncestryDNA cost around $100-200. They analyze about 700,000 specific genetic markers – it’s like getting a glimpse into your genetic story rather than a full novel. For basic insights into ancestry and health, they offer excellent value.
For more comprehensive consumer testing, companies like Nebula Genomics offer whole genome sequencing starting at around $300. This gives you 100 times more data than basic tests, including rare genetic variations and detailed analysis of ancestry.
Medical-Grade Mapping
When doctors order genetic testing, they typically want a more detailed analysis. Clinical-grade genome sequencing runs from $1,000-3,000, depending on the specific tests needed. This level provides the accuracy and depth needed for medical decisions. Specialized panels that focus on specific conditions (such as cancer genes or heart disease) often cost $500-1,500. These targeted approaches provide detailed information about genes related to specific health concerns.
Research-Level Mapping
For the most comprehensive analysis – including structural variations, epigenetic markers, and advanced annotations – the cost can reach $5,000-10,000. This level is usually reserved for complex clinical cases or research studies.
Gene mapping is easier to access now than it was 20 years ago, and you can often find this information for less than the cost of a smartphone. For students who want to learn about genetics through fun experiments and activities, “Basic Genetics and Genomics Kit” is very helpful. Furthermore, it’s great for anyone who wants to understand genetics by doing hands-on work.
What Genes Mapping Reveals About Human Health
Gene mapping gives us a lot of information about our bodies, health, and family history. However, we need to know what it can and can’t do. You can think of your genetic map like a weather forecast: it is very helpful for planning, but it does not promise what will happen for sure.
1. Health and Disease Risk
Your genes can reveal whether you are more likely to develop health problems such as heart disease, diabetes, some cancers, and Alzheimer’s. For example, mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes can increase your risk of breast and ovarian cancer. However, just because you have these mutations doesn’t mean you will get cancer. It’s a warning that helps you be prepared.
Gene mapping can also tell if you carry genes for certain conditions, such as cystic fibrosis, even if you don’t have the condition. This is important if you want to start a family.
2. Personalized Medicine Insights
An interesting application of gene mapping is pharmacogenomics, which looks at how our genes influence how we respond to medications. Our genes help predict whether we will react quickly or slowly to certain medications, which can prevent adverse reactions or ineffective treatments. Some people need higher doses of blood thinners, while others need less – your genes may explain why.
Important: This report is for educational purposes. Always consult healthcare professionals before making medical decisions based on genetic information.
3. Traits and Characteristics
Gene mapping can also reveal some interesting things about your physical traits. Your genes can influence things like whether cayenne pepper tastes like soap to you, whether you have curly hair, or whether you can taste bitter flavors that others can’t.
Important Limitations
Gene mapping can’t accurately predict complex conditions. For example, autism involves many genetic factors and environmental influences. Although gene testing can find some risk factors, it can’t guarantee whether someone will have autism. Similarly, traits such as intelligence and personality are shaped by many genes and life experiences.
From Human Genome Project to Today’s Genomic Advances
The journey to map the human genome is a timeless story of incredible scientific ambition. It all began with the Human Genome Project (HGP), a monumental international research effort launched in 1990. Its goal was to sequence and map all of the genes in humans.
- Key Milestones: The Human Genome Project produced the first rough version of the human genome in 2003, which was a major achievement. By 2006, they had created a nearly perfect map of a complete chromosome.
- The Next Challenge: For many years, scientists used a reference genome, which was a basic map of human DNA. However, this map did not show the full range of human genetics.
- 2025 Breakthroughs: In July 2025, researchers shared the first “pangenome” reference, a new type of genetic map created from the ancient DNA of many people from different backgrounds. The pangenome is much more detailed and reveals many differences in DNA between people. The new map is an important step towards personalized medicine and understanding human evolution. It’s the closest we’ve come to a complete map, but there’s still more work to be done in mapping human genes.
Today’s ability to map genes will seem like magic to scientists on the Human Genome Project. We have moved from wondering, “Can we map the human gene?” to asking, “How can we use this information to improve lives?” The next part of this story will bring even more amazing revelations.
Benefits of Mapping the Human Genes
As advances have been made in gene mapping, its benefits have also increased. It has helped a lot in advancements in medicine, in addition to being helpful in treating an individual, and there has also been a lot of improvement in the field of diagnosis. Let’s now take a step-by-step look at the benefits of human genes mapping.
1. Developments in Medical Diagnosis
It has greatly helped doctors in diagnosing complex diseases. In the past, when a person was sick, doctors would take a long time to diagnose the disease, which often resulted in deaths. However, since the development of human genes mapping technology, diagnosing diseases has become easier, and with the help of which, any treatment for a person has become effective quickly and efficiently.
Prenatal genetic testing can now detect conditions like Down syndrome with over 99% accuracy using a simple test of the mother’s blood. This early information is very helpful because it helps families make smart choices and prepare for their child’s needs in advance.
2. Personalizing Treatment Strategies
Another great benefit of human genes mapping is that it has greatly improved cancer treatment. Doctors can decide by looking at the type of genes present in tumors whether the chances of cancer are high or low. This means that diagnosis has become easier, which greatly helps in cancer treatment. With its help, doctors can focus only on cancerous cells, which has made it possible to treat cancer without harming other healthy cells. This is a great advantage because until some time ago, cancer treatment was considered very difficult and many deaths occurred. However, due to advances in gene mapping, it has now helped in the treatment of cancer to a considerable extent.
As pharmacogenomics is about choosing the right drugs based on a person’s genes. This helps avoid adverse drug reactions and makes treatments work better. Some hospitals now check patients’ genes before giving them certain drugs, which helps reduce side effects and get the right dose from the start.
3. Accelerating Drug Development
Drug companies use genome mapping to find new drug targets and to understand why some drugs work for some people but not for others. This helps them create better treatments with fewer side effects.
Genome mapping also helps drug repurposing, which means finding new uses for old drugs based on genetic information. This approach could provide patients with treatments much faster than creating new drugs from scratch.
Conclusion
Human genes mapping has gone from a distant goal to a common practice, helping us understand health, family history, and human differences. What used to cost a lot of money has now become affordable for many, giving more people access to genetic information that can help them make better medical choices and connect families.
The technology is improving. New discoveries, such as tailored cancer treatments and family connections around the world, are just the beginning of what gene mapping can do. As prices fall and new capabilities grow, human genes mapping could soon become as routine as blood tests, offering personalized health advice throughout our lives.
If you want to know more about genetics and science, stay connected with us. And don’t forget to express your thoughts in our comment box.
Recommended Reads for Curious Minds
1. The Gene: An Intimate History
“The Gene: An Intimate History” by Siddhartha Mukherjee is a well-written book about genetics, covering topics from Mendel’s experiments with peas to today’s gene therapy. It’s great for learning about the personal stories behind genetic discoveries.
Check it out here: The Gene: An Intimate History
2. Genome: The Autobiography of a Species in 23 Chapters
“Genome: The Autobiography of a Species in 23 Chapters” by Matt Ridley is an easy-to-understand book that takes you through each human chromosome. It explains what genes are and how they affect our lives in simple, clear language.
Check it out here: Genome: The Autobiography of a Species in 23 Chapters
3. The Code Breaker
“The Code Breaker” by Walter Isaacson tells the interesting story of CRISPR gene editing and Jennifer Doudna’s important discoveries, showing how new genetic tools are changing medicine and biology.
Check it out here: The Code Breaker
4. She Has Her Mother’s Laugh
“She Has Her Mother’s Laugh” by Carl Zimmer looks at how traits are inherited. It goes deeper than just genes and shows how characteristics are passed down in unexpected ways.
Check it out here: She Has Her Mother’s Laugh
Frequently Asked Questions
Scientists use three main mapping approaches: genetic mapping (studying inheritance patterns), physical mapping (identifying exact chromosomal locations), and sequence mapping (reading actual DNA letters). Each provides different levels of detail and gives specific research or clinical purposes.
Today, the most popular methods are SNP array analysis (used in genetic testing for consumers), whole genome sequencing (for detailed analysis), and targeted gene panel testing (which looks at specific health issues). These methods consider cost, detail, and usefulness.
Yes! Scientists finished the first full human genome sequence in 2022, filling in missing parts from the earlier Human Genome Project. This sequence is for one person. The 2025 Human Pangenome Project will offer complete sequences that show human diversity worldwide.
Personalized medicine is the biggest benefit. Gene mapping helps doctors give treatments that are better suited to each person’s genes, making them work better and causing fewer side effects. This method is already helping save lives in cancer treatment and stopping harmful drug reactions.
Genome sequencing can find some genes linked to autism risk, but it can’t predict autism for sure. Autism is affected by many genes and environmental factors, which makes prediction very hard. Genetic testing is more helpful for understanding autism after a diagnosis, rather than predicting it.