In our digital age, encryption plays a crucial role in keeping our important information secure, just think about your online banking or personal details. But here’s the catch: quantum computers are on the horizon, and they’re way faster than the computers we use today. They could potentially crack our current encryption methods, like RSA and ECC, with ease. These systems are based on complex math problems, but guess what? Quantum computers can solve those problems very quickly. Experts, including folks from IBM, are saying we might see these powerful machines by 2030. So, what do we do about it? Well, that’s where post-quantum cryptography (PQC) comes in. It’s being developed to create new encryption methods that can stand up to the quantum threat.
In this blog post we will dive into PQC, why it’s super important for companies to act fast, and how they’re gearing up for these changes. It’s aimed at IT professionals, business leaders, and tech enthusiasts alike to help everyone figure out the next steps. Just keep in mind,
Quantum computers could make today’s encryption useless by 2030
That’s a wake-up call for all of us! You know?
Before diving deeper into how companies are preparing for the quantum threat, check out our detailed guide on the basics of post quantum cryptography to build a strong foundation.
Understanding Post-Quantum Cryptography
Post-quantum cryptography, or PQC for short, is all about creating secure codes that can stand strong against the looming threat of quantum computers. Traditional public-key methods rely on some tough math problems, like factoring large numbers, to keep our data safe. But PQC? It’s a different ballgame. It’s built on mathematical approaches that are specifically crafted to withstand quantum attacks. Take lattice-based cryptography, for example. It’s quite popular within the PQC realm and uses these intricate grid-like structures that are tricky to crack, even for the most advanced quantum machines. There are other approaches too, such as multivariate cryptography, hash-based cryptography, and code-based cryptography. Every option offers distinct benefits.
Now, the National Institute of Standards and Technology or NIST, as we often call it, has been crucial in developing standard methods for post-quantum cryptography. Back in August 2024, they rolled out FIPS 203, 204, and 205. These new standards are all about the CRYSTALS-Dilithium, CRYSTALS-KYBER, and SPHINCS+ algorithms. Then, on March 11, 2025, NIST added HQC to their list of recognized methods. This really helps lay a solid foundation for encryption that can withstand the quantum storm on the horizon. The table below breaks down how traditional methods stack up against these new PQC techniques.
| Algorithm Type | Vulnerable to Quantum Attacks | PQC Alternative |
|---|---|---|
| RSA | Yes | CRYSTALS-KYBER |
| ECC | Yes | CRYSTALS-Dilithium |
| Hash-based | No | SPHINCS+ |
Why Companies Need to Act Now
While the quantum threat isn’t exactly knocking down our doors right this minute, it could definitely stir up some serious trouble down the line. You’ve probably heard of the “harvest now, decrypt later” tactic. Adversaries can store encrypted data now and wait until they have tools to break it later. This represents a pretty big risk for crucial areas like finance and healthcare, where keeping sensitive info safe for the long haul is absolutely indispensable. Just think about it—financial records need to stay under lock and key for years, which makes them prime targets for those looking to exploit vulnerabilities.
Speaking of risks, there’s a chart below that lays out the potential costs of breaches associated with quantum tech. It really drives home the financial stakes involved.
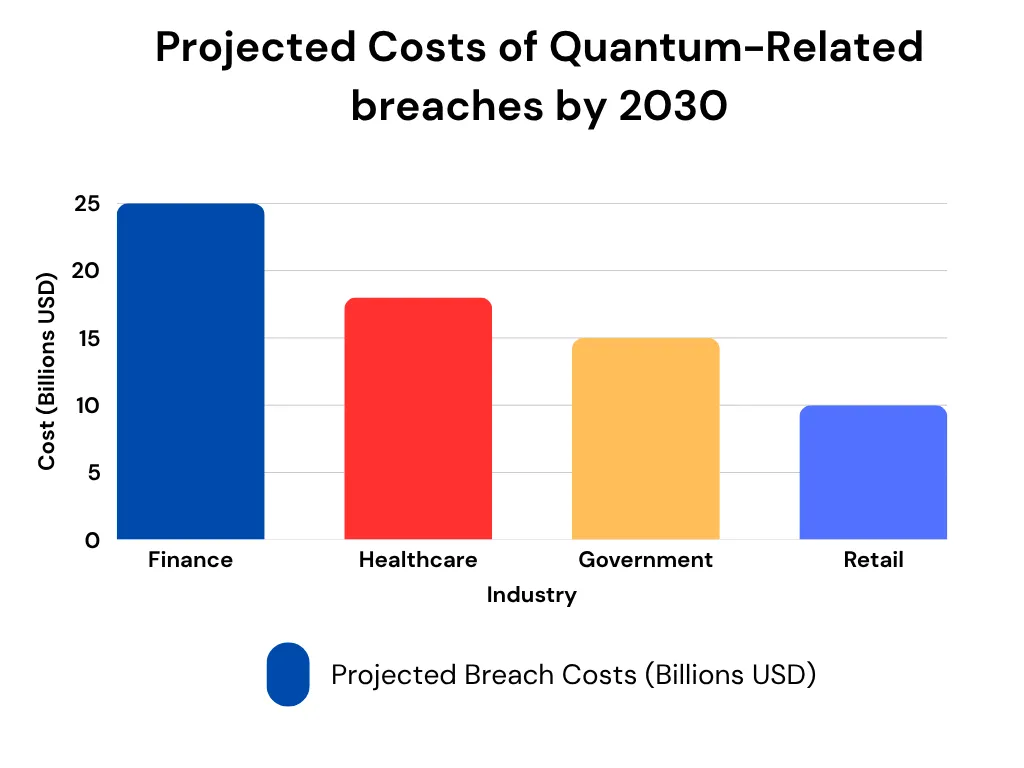
On top of that, regulations are ramping up. The European Union’s Cybersecurity Act is rolling out requirements for quantum-safe practices, and the U.S. National Security Agency is urging federal agencies to transition to post-quantum cryptography. Getting on board with these measures sooner rather than later not only helps mitigate risks but also ensures compliance and fosters trust with partners. It’s all about being proactive.
The “Harvest Now, Decrypt Later” Risk
It’s kind of alarming how adversaries can stash away encrypted data now, just biding their time until quantum computers come along to break it open. This is especially concerning for industries that deal with sensitive information. Think about it: if we don’t use quantum-safe encryption, things like healthcare records or government communications could be at serious risk. It’s definitely something we need to pay attention to!
Regulatory and Compliance Drivers
With all these new regulations popping up, companies are really starting to focus on post-quantum cryptography. It’s interesting to see how the EU’s directives and the NSA’s guidelines are kind of paving the way for a worldwide move towards quantum-safe standards. Take a look at the table below; it highlights some key regulations you might want to keep an eye on.
| Region | Regulation | PQC Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| EU | Cybersecurity Act | Encourages quantum-safe measures |
| U.S. | NSA Guidelines | Recommends PQC transition |
How Companies Are Preparing for Post-Quantum Cryptography
When it comes to post-quantum cryptography, the big players in tech are really stepping up. Take Microsoft, for instance. Back in May 2025, they announced that they had PQC features ready for Windows Insiders and users on Linux. This means folks can actually test out secure encryption that stands up to the threat of quantum computers. And then there’s Google, which has integrated PQC methods into Chrome to see how effective they really are. And let’s not forget IBM; they’re also diving into some robust PQC solutions and lending a hand with the standards set by NIST.
However, it’s not just the giants getting in on the action. Smaller companies are joining the fray, often by partnering with cybersecurity firms that specialize in post-quantum cryptography solutions. Even cloud services like AWS are starting to include quantum-safe methods in what they offer, and they’ve laid it all out in their security blog.
Strategies for Smaller Enterprises
So, smaller companies have a great opportunity here. They can tap into cloud-based PQC solutions or team up with vendors like Entrust. By doing this, they can really cut down on the need for specialized in-house skills. And if you check out the handy checklist graphic below, you’ll find some solid steps to get ready for PQC. It covers everything from auditing your systems to testing out algorithms.
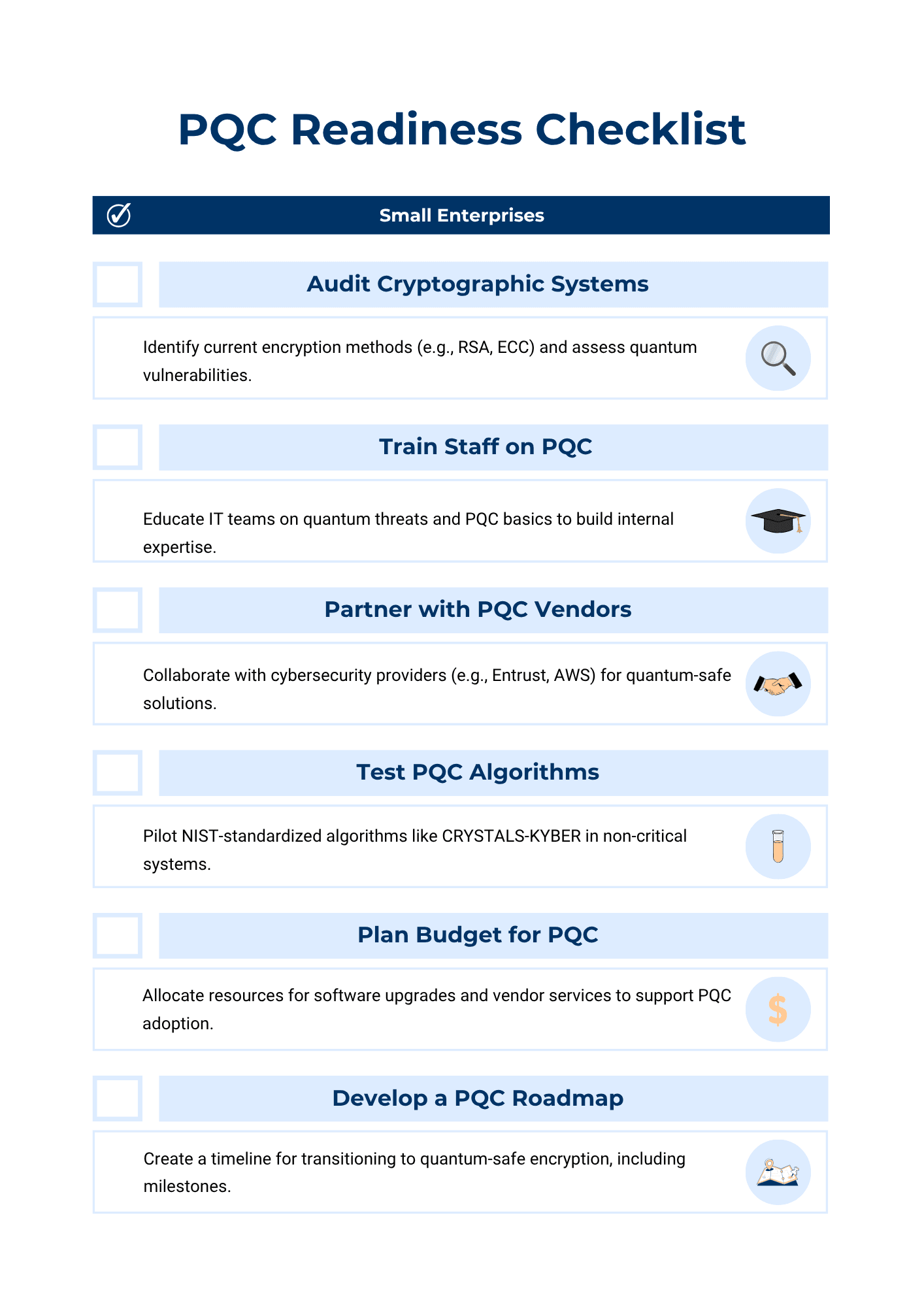
Steps to Start Your Post-Quantum Cryptography Journey
So, if companies are looking to kick off their journey into post-quantum cryptography, the first step is pretty straightforward: conduct a cryptographic inventory assessment. This helps pinpoint any weak spots in their current encryption methods. There are some handy tools out there, like those offered by NIST, that can really help with this.
Once you’ve got a handle on what needs fixing, the next move is to create a PQC roadmap. This should include clear timelines for things like piloting new solutions, training your team, and finally rolling everything out.
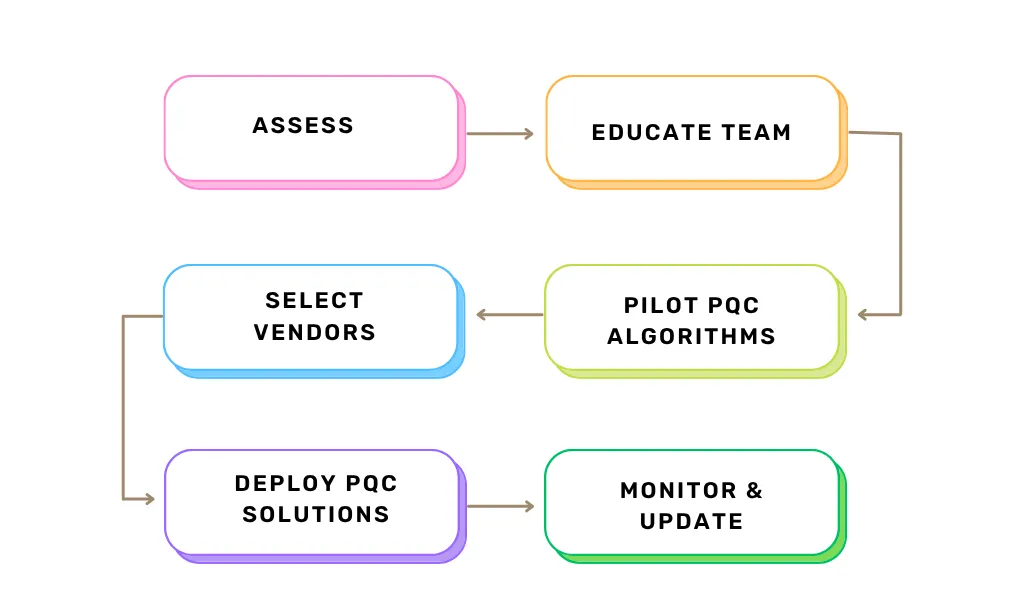
Building a Post-Quantum Cryptography Roadmap
A PQC roadmap should include:
- Assess Cryptographic Inventory
- Education: Train staff on quantum risks and PQC.
- Pilot Projects: Test PQC algorithms in non-critical systems.
- Vendor Selection: Partner with PQC solution providers.
- Deployment: Roll out PQC gradually, starting with critical systems.
- Monitoring: Update systems as new standards emerge.
The timeline graphic below illustrates a sample roadmap.
Conclusion: Securing Tomorrow, Today
Quantum computing is on the horizon, and honestly, it’s a game changer that could seriously threaten our online security. We really need to get moving on this. Enter post-quantum cryptography, or PQC for short. It’s a way to build super strong encryption that can keep our data safe for a long time.
Now, companies that choose to overlook this risk, they might end up dealing with data leaks, legal headaches, and a tarnished reputation. Not a great place to be. But here’s the silver lining: businesses can turn this challenge around. By taking a hard look at their current security systems, figuring out how to transition to PQC, staying adaptable with their security strategies, and getting involved in the NIST PQC standards, they can really boost their cybersecurity. After all, the safety of our digital communications tomorrow hinges on what we do today.
Frequently Asked Questions
Post-quantum cryptography (PQC) develops encryption algorithms that can resistant to quantum computer attacks, unlike traditional methods like RSA. It ensures data security as quantum computing progresses, using standards like NIST’s CRYSTALS-KYBER.
Quantum computers could break current encryption, enabling “harvest now, decrypt later” attacks. Acting now with quantum-safe encryption protects sensitive data in industries like finance and healthcare.
Companies like Google and IBM test PQC algorithms, while smaller firms use cloud-based solutions. PQC implementation involves auditing systems and adopting crypto-agile frameworks.
NIST’s PQC standards, like CRYSTALS-Dilithium and SPHINCS+, are quantum-resistant algorithms, that are finalized in 2024–2025. They help companies in adopting secure and quantum-safe encryption.