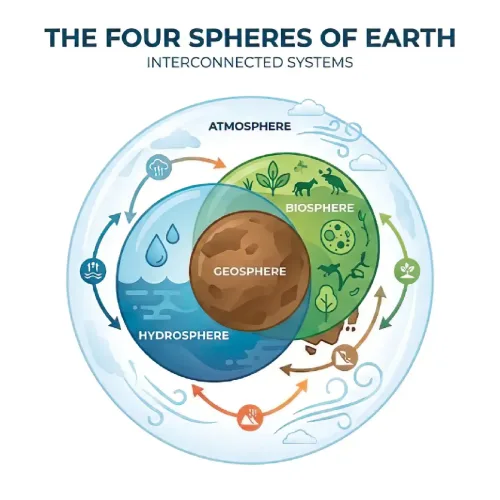
Microbes are all around us. They may be small, but they play an important role in the environment, medicine, and industry. These small living organisms are classified into different groups based on their characteristics. Today, I will walk you through the classification of microorganisms in an easy and understandable way. We will examine the major types of microorganisms, from bacteria to fungi. We will explore their examples and their importance in everyday life.
What are Microorganisms?
Microorganisms are the organisms that are so small so that they can only be seen with a microscope. They exist everywhere, leading from the soil and water to the air we breathe. You may have heard of bacteria, viruses, fungi, and algae. However, there are more groups that we are going to explain today.
Microorganisms are like a large library of books. If there is no way to organize them, it will be difficult to find the right book. Similarly, scientists need to classify the many types of microbes on Earth to understand them.
Classification of microorganisms serves several important purposes:
- Disease identification: Doctors can quickly identify harmful bacteria causing infections
- Drug development: Pharmaceutical companies use classification to find new sources of antibiotics
- Food safety: Food inspectors classify microbes to prevent foodborne illness
- Environmental protection: Scientists classify microbes that clean up oil spills and other pollutants
There are many different types of tiny organisms called microorganisms. Scientists have discovered more than 1 million species, but they think there could be more than 1 trillion. Each one is important for the continuation of life on Earth.
Classification of Microorganisms Based on Cell Type
1. Prokaryotes
Prokaryotic is the type of microorganisms that are without of a distinct nucleus. Their genetic material floats freely inside the cell. This category of microorganisms includes bacteria and archaea.
- Bacteria: These are the microorganisms that are found almost everywhere on earth. From gut bacteria that help us to digest food, to bacteria that decompose waste, they are very important for many processes.
- Archaea: Archaea are similar to bacteria but vary in genetic style and metabolic process. They are often found in extreme environments such as hot springs or in deep sea vents.
2. Eukaryotes
This type of microorganisms, unlike prokaryotes, have a defined nucleus. Examples of eukaryotic microorganisms include fungi, algae, and protozoa.
- Fungi: These microorganisms include mold, yeast, and mushrooms. Most of them are beneficial, such as yeast is used in baking, while others can cause infections such as athlete’s foot.
- Algae: are mainly found in aquatic environments, algae are essential for the production of oxygen through photosynthesis.
- Protozoa: These are single celled organisms and are mostly found in water or soil. Some protozoa, such as amoeba, are harmless, while others can cause diseases such as malaria.
Classification of Microorganisms Based on Oxygen Requirement
Microorganisms can also be classified on the basis of oxygen requirement.
- Aerobic Microorganisms: These organisms require oxygen to survive. These include many bacteria that can help in processes such as decomposition.
- Anaerobic Microorganisms: These microorganisms do not require oxygen and, in some cases, can even die in the presence of oxygen. Anaerobes play an important role in environments such as deep soil or gut.
Classification of Microorganisms Based on Nutrition
Microorganisms can be classified based on how they obtain food. Some of them produce their own food, while others rely on external sources.
1. Autotrophs
Autotrophic microorganisms make their food from simple substances such as carbon dioxide. They are further divided:
- Photoautotrophs: Use sunlight for energy. Cyanobacteria are an example of Photoautotrophs, and they play an essential role in the production of oxygen in aquatic systems.
- Chemoautotrophs: These microorganisms obtain energy from chemical reactions. Archaea live in extreme conditions, such as deep-sea vents, are the types of this group.
2. Heterotrophs
Heterotrophic microorganisms rely on organic matter for their food rather than producing it themselves. They break down dead organisms, help in reducing to recycle nutrients back into the environment. Many bacteria and fungi act as heterotrophs, which play an important role in decomposition. To make it clearer, take a look at the table below for a better understanding.
| Classification | Types | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Type | Prokaryotes | Microorganisms without a distinct nucleus. | Bacteria, Archaea |
| Eukaryotes | Microorganisms with a defined nucleus. | Fungi, Algae, Protozoa | |
| Oxygen Requirement | Aerobic | Require oxygen for survival. | Decomposing bacteria |
| Anaerobic | Do not require oxygen; may even die in its presence. | Some gut bacteria, Clostridium | |
| Nutrition | Autotrophs | Produce their own food. | Cyanobacteria, Archaea |
| Heterotrophs | Rely on organic matter for food. | Many bacteria, Fungi |
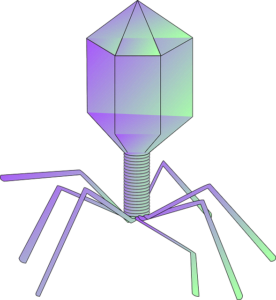
Viruses
Viruses often come into discussions about microorganisms, but they vary significantly from others. Unlike living organisms, viruses can’t reproduce without a host. They occupy plants, animals, and even bacteria (bacteriophages). For example, flu viruses and HIV show this unique trait.
Modern Phylogenetic Classification
The way we classify small organisms has changed dramatically with the use of DNA sequencing. Instead of just looking at their characteristics, scientists can now study their genetic makeup. This new method uses a piece of RNA called 16S ribosomal RNA (rRNA). Ribosomes help make proteins, and all living things have them. The 16S rRNA gene changes slowly, making it good for comparing different types of microbes.
Here’s how 16S rRNA sequencing works:
- DNA extraction: Scientists extract genetic material from microbial samples
- PCR amplification: Special techniques multiply the 16S rRNA gene millions of times
- Sequencing: Machines read the genetic code letter by letter
- Database comparison: Computers compare sequences against known species
- Phylogenetic analysis: Software builds family trees showing evolutionary relationships
This new method showed surprising results. Many microbes that looked the same under a microscope were actually different species. Now, scientists use phylogenetic trees to classify microbes. These trees show how species are related, with similar species on nearby branches. If the branch between two species is long, it means they are more genetically different.
Practical Applications of Microbial Classification
1. Medical and Public Health Applications
Classification identifies pathogens (for example, MRSA as a Staphylococcus aureus variant), enables targeted antibiotics and outbreak tracking.
2. Industrial and Environmental Uses
In biotech, classified microbes such as Pseudomonas enable bioremediation. Classified fungi aid in the production of enzymes.
| Microbe | Application |
|---|---|
| Lactobacillus | Yogurt production |
| Pseudomonas | Bioremediation |
| Saccharomyces | Brewing/fermentation |
FAQs
Microorganisms are the tiny organisms that are too small to be seen with the naked eye. These organisms include bacteria, fungi, viruses, protozoa, and algae.
Bacteria play various roles, such as help in digestion, producing vitamins and decomposing organic matter. Some bacteria can also cause diseases.
Viruses are non-cellular objects that require a host to replicate, unlike other microorganisms that can independently survive and reproduce.
Microorganisms are classified based on their shape, size, cell structure, mode of nutrition, and genetic makeup. These criteria help scientists group them into categories like bacteria, fungi, viruses, and protozoa.
Classification helps scientists see how different microorganisms are related. It also makes it easier to study, identify, and treat diseases caused by these microbes.
Yes, microorganisms can be grouped by where they live, such as soil, water, or inside other organisms. This helps in understanding their role in different environments and ecosystems.
Conclusion
Microorganisms may be small, but they have a huge impact on our lives. They break down waste, they can cause disease, and produce oxygen, each of them is playing its role. As we learn more about their taxonomy, we can easily differentiate them. We will know which type is more beneficial. Then, we could appreciate their actions. This knowledge will help us to understand how they are constantly developing the surrounding environment.
Recommended Microbiology Resources
To better understand how microorganisms are classified, check out these great resources that are ideal for students, teachers, and anyone interested.
- Brock Biology of Microorganisms by Michael Madigan
- The Invisible Kingdom by Idan Ben-Barak
- Microbiology QuickStudy by Frank Miskevich